Can you reduce one or more of the six progress hurdles to enable Seekers to make more progress?
What we’re thinking
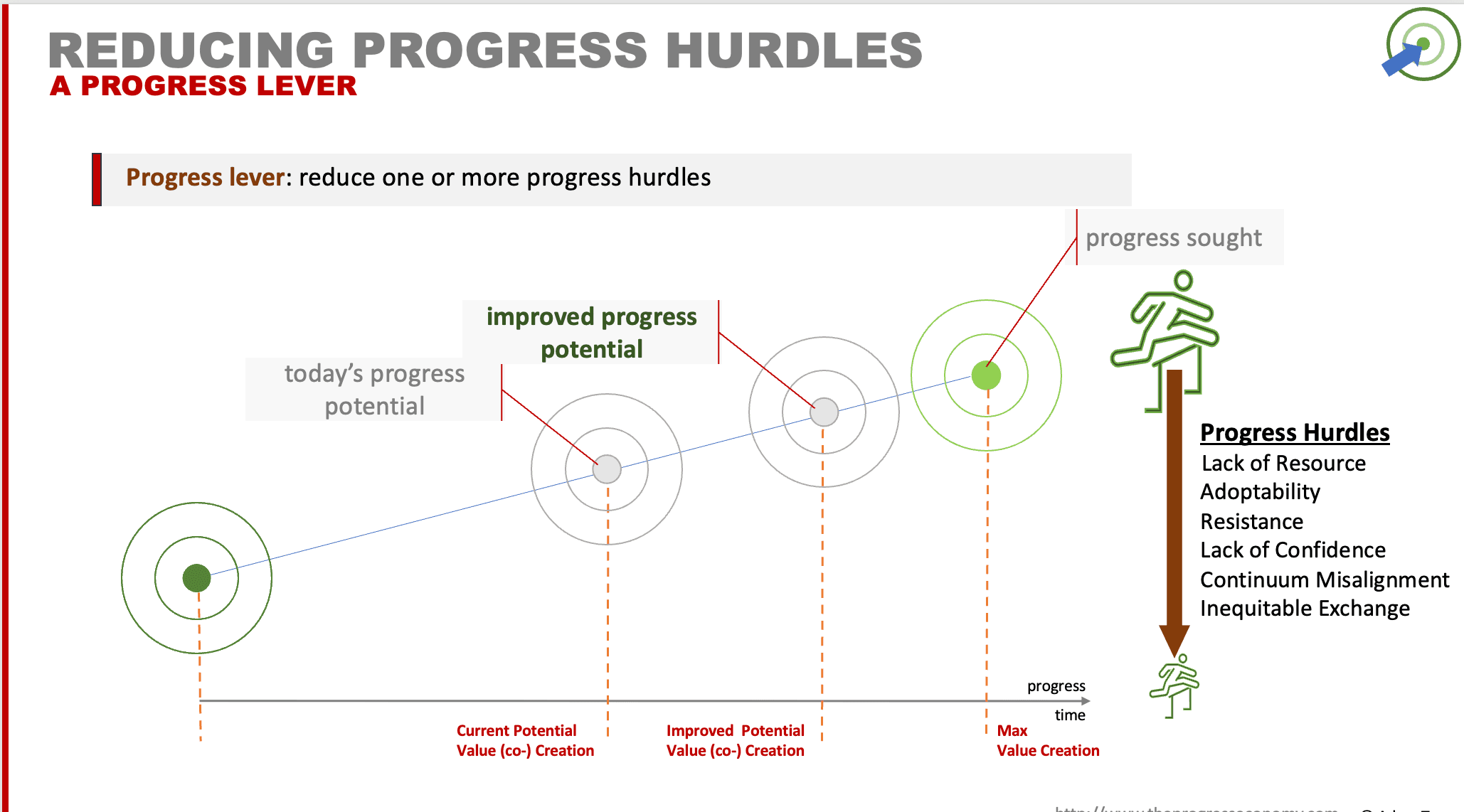
One of the four innovation outcomes is a proposition that reduces one or more of the six progress hurdles.
Is your innovation reducing the lack of capabilities or is more adoptable with less resistance? Are you aligning with you Seeker’s position on the relieving to enabling continuum? Or have you innovated the business model to reduce the inequitable exchange fear of unfairness?.
Lowering progress hurdles
An outcome of innovation is a progress proposition that lowers one or more of the 6 progress hurdles
Our third innovation outcome is reducing one or more of the six identified progress hurdles.
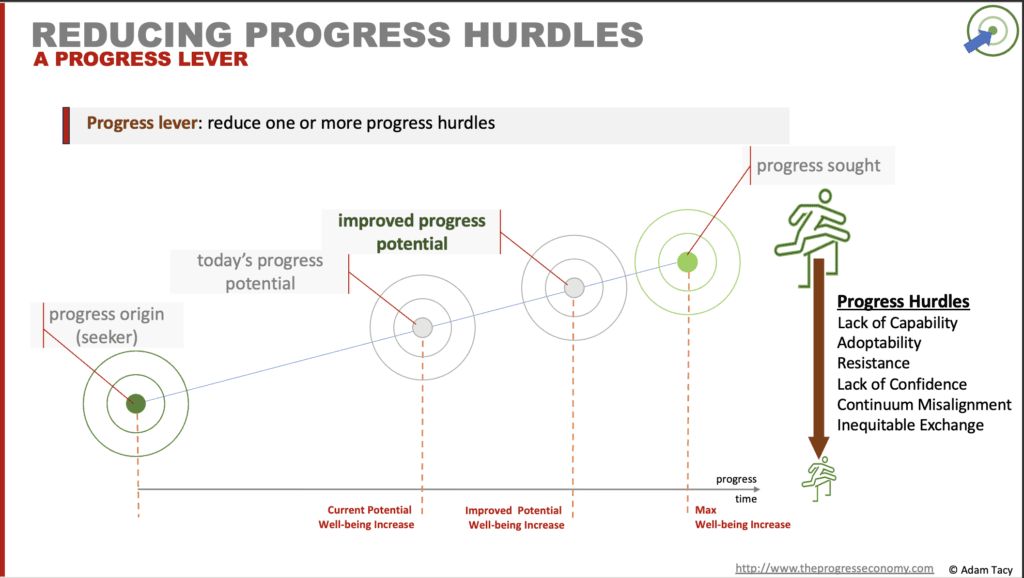
These hurdles are the aspects that may hinder a Seeker making progress. The foundation hurdle being a lack of capability (skills, knowledge, physical, natural, and abstract like time). As we’ve seen, progress propositions aim to reduce this foundation hurdle; but they introduce five additional hurdles.
A Seeker’s judgment of progress potential, with your proposition, rests on how high they perceive these six hurdles to be. The higher they feel the hurdles are, the lower their perceived potential for progress. By lowering the perceived height of those hurdles, we increase the likelihood that the Seeker chooses to engage your proposition (therefore the more likely your are to get the exchange you are after).
| progress lever | discussion |
|---|---|
| reduce lack of capability | this is the foundation hurdle and the general purpose of any proposition is to lower it; can you reduce that lack further? |
| increase adoptability | this hurdle reflects Rogers’ classic adoptability factors (compatibility etc); can you increase those and therefore reduce this hurdle? ➠ the classic example here is the QWERTY nature of your keyboard. Introduced to slow down typists on typewriters and reduce mechanical jams, it has no need on computers, but we have qwerty keyboards for familiarity. Even on digital mobile touch screens, QWERTY persists, now to provide compatibility with computers, |
| reduce resistance | it is not just a case of getting an innovation adopted; some innovations are resisted on a sliding scale for reasons identified in this hurdle; can you innovate to minimise resistance to your proposition? ➠ Google failed with this with their Google Glass v1; Rogers’ innovation adopter types didn’t give much resistance, but the “early majority” and general public did – you may remember the users acquired the name “glassholes”. |
| reduce lack of confidence | how can you increase the confidence of the Seeker in you and your proposition to reduce this hurdle? Are their branding aspects your can extend from other propositions you have? ➠ Apple do this when moving into new categories, they leverage power of their brand; Amazon had users confidence when breaking out of selling books to selling services as they were offering what they used; In contrast, it might be a challenge for, say, McDonalds to start selling you cars. |
| reduce continuum misalignment | where is the Seeker positioned on the enabling-relieving progress continuum; and can you innovate to move your proposition’s position closer? ➠ the “shift to the service economy” is an example; here we see Seekers moving towards the relieving end of the continuum and propositions need to keep up. But be aware, Seekers do go the other way when they want to gain skills, or do things themselves. |
| reduce inequitable exchange | this is high if the Seeker perceives the effort they need to give (usually elsewhere to gain service credits) is not fair compared to the amount of effort you want in exchange for your service. For simplicity, you can see this as price. It is reduced through business model innovation; rather than look for a one time exchange of maximum service credits (eg money), can that be spread over time (subscription, credit, buy-now-pay-later, etc) or other sources for those credits (subsidised, ad-based, collect data for sale, etc) ➠ Spotify shifted business model of music industry from single purchase for dedicated context to subscription based payments for access to much wider content, |
There are links between these hurdles, where lowering one can higher another. For example, offering to lower the lack of capability likely increases your exchange requirements (which may be interpreted by the Seeker as highering the inequitable exchange hurdle).
Our final innovation outcome moves beyond aligning on progress journey and reducing hurdles to making progress. It addresses the need for a Seeker to recognise the well-being increase that emerges as progress is made.
Let’s progress together through discussion…